Acids and Bases
PH Scale
Acids are Proton Donors. An acidic solution has a pH number less than 7.
Bases are Proton Acceptors. A Basic solution has a pH number greater than 7.

From Text Books
Indicator Colour Change
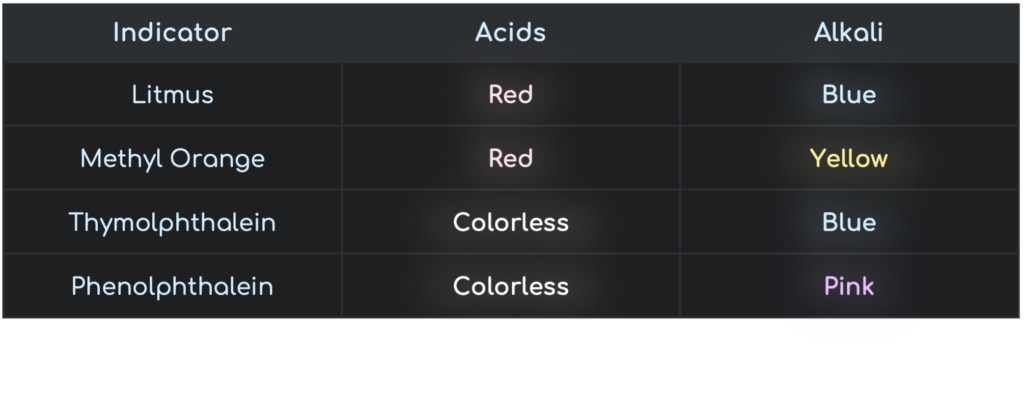
From Text Books
Difference between Strong Acids and Weak Acids
Acids contain Hydrogen ions. In solutions of strong acids, all the molecules become ions. In solutions of weak acids, only some do. The higher the concentration of hydrogen ions, the lower the pH.
Difference between Strong Bases and Weak Bases
Bases contain Hydroxide ions. If Solution A has a higher PH than Solution B, Solution A contains the most ions. The higher the concentration of hydroxide ions, the higher the pH.
From Text Books
Typical Acid Reactions
- With Metals: Acid + Metal ➜ Salt + Hydrogen
- With Bases: Acid + Base ➜ Salt + Water
- With Carbonates: Acid + Carbonate ➜ Salt + Water + Carbon dioxide
Typical Base Reactions
- Bases react with acids, and give salt and water.
- Bases such as sodium, potassium, and calcium hydroxides react with ammonium salts, giving out ammonia gas.
Neutralisation
Neutralisation is a reaction with acid that gives water as well as a salt. So the reactions of bases and carbonates with acids are neutralisations.
From Text Books
Oxides
From Text Books
Oxides are compounds containing oxygen and another element. In general, metals react with oxygen to form basic oxides. (Examples: Copper(II) oxide, CuO + 2HCl ➜ CuCl2 + H2O). Non-metals react with oxygen to form acidic oxides. (Examples: C + O2 ➜ CO2 OR S + O2 ➜ SO2)
© Copyright 2024 - Made with Passion
