Periodic Table
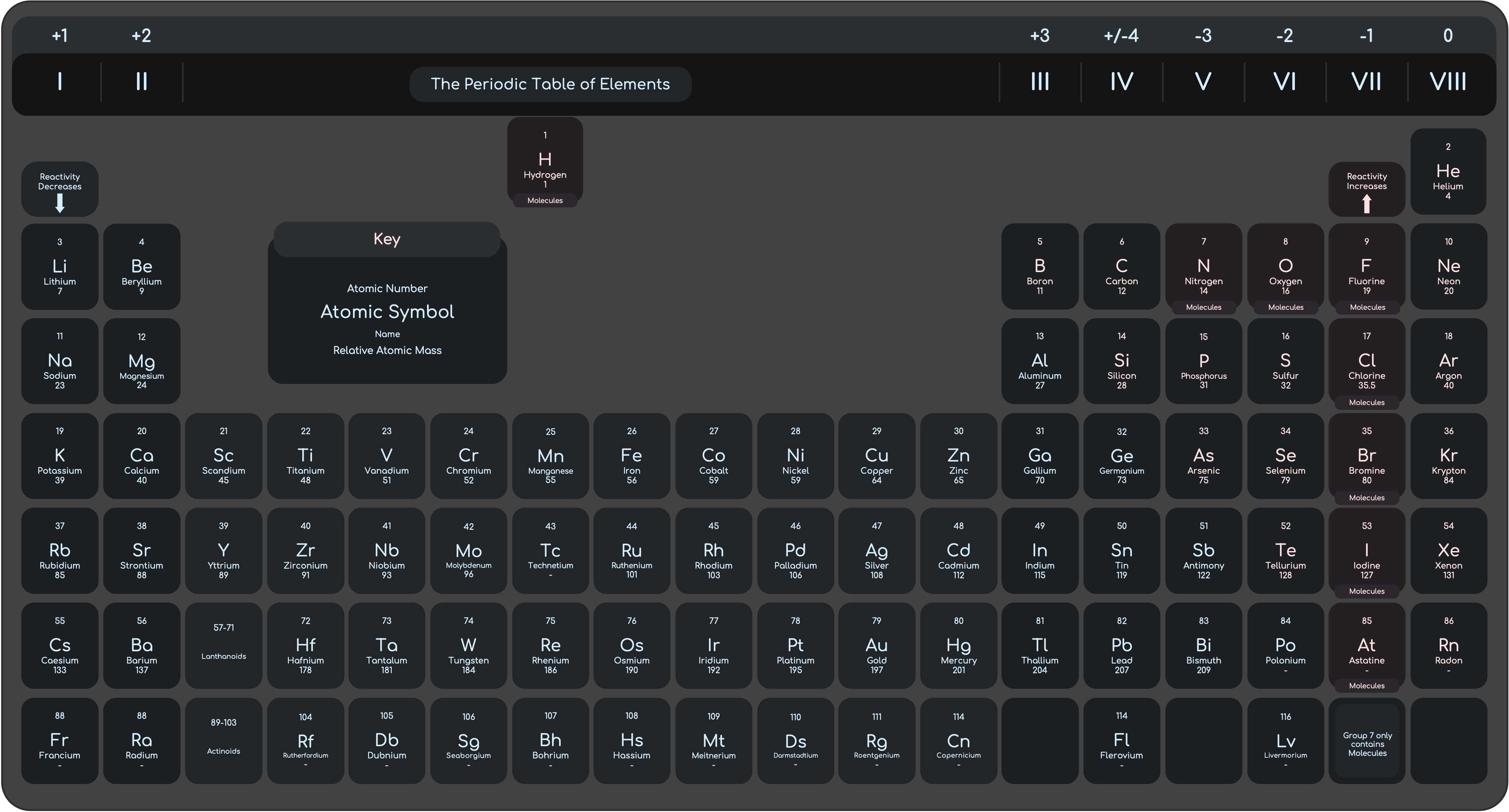
Group I (The Alkali Metals)
Alkali Metals are soft silvery metals. They only have 1 electron in the outer shell.
Physical Properties
Softer than most metals, Lighter than most metals, have low density and have low melting points.
- Density Increase down the group.
- Melting Point decreases down the group.
Chemical Properties
Alkali metals react vigorously with water, burst into flame with chlorine and can react with oxygen to form oxides. Alkali metals produce white solids after reactions, which can dissolve in water to form a colourless solution.
- Reactivity Increases down the group
From Text Books
Group VII (The Halogens)
Physical Properties
All halogens have different colour and all of them are poisonous. They form diatomic molecules.
- Density Increase down the group.
- Boiling Point Increase down the group.
Chemical Properties
- Reactivity Decreases down the group.
- They can react with metals and non-metals.
From Text Books
Properties of the Transition Elements
From Text Books
Physical Properties
- Higher Density when compared with Group I elements
- Higher Melting point when compared with Group I elements
- Hard and Strong unlike group I elements
- Good Conductors of heat and electricity
Chemical Properties
- Less reactive than Group 1 Elements
- Transition elements do not show clear trend in reactivity
- Most Transition elements form coloured compounds
- Transition elements and their compounds can act as catalysts
- Variable Oxidation States
Reversible Reactions and Equilibrium
Shifting of Equilibrium
Changing Concentrations
- Adding more reacting or removing product means yield ↑
Changing Temperature
- Forward Reaction Exothermic: Temperature ↑ means yield ↓
- Forward Reaction Endothermic: Temperature ↑ means yield ↑
Changing Pressure (reactions which involve gasses)
- Fewer molecules on the right of the equation: Pressure ↑ means Yield ↑
- Fewer molecules on the left of the equation: Pressure ↑ means Yield ↓
Adding Catalyst
From Text Books
Reversible Reactions and Equilibrium
Reversible Reactions in a closed system are in equilibrium when
- The Forward and the reverse Reactions take place at the same rate.
- The Concentrations of reactants and products stay the same.
From Text Books
Haber Process
Haber Process is used to produce Ammonia. The Forward Reaction is Exothermic and the Reverse Reaction is endothermic.
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ⇌ 2NH3 (g)
From Text Books
Contact Process
Contact Process is used to produce Concentrated Sulphuric Acid. The Forward Reaction is Exothermic and the Reverse Reaction is endothermic.
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) ⇌ 2SO3 (g)
From Text Books
Extraction of Metals
Extraction of Iron

From Text Books
Extracting Aluminium
At the Cathode:
- 4Al3+ + 12e– ➜ 4Al (Reduction)
At the Anode:
- 6O2- ➜ 3O2 + 12e– (Oxidation)
- C + O2 ➜ CO2 (Oxidation of Carbon)
Overall Reaction:
2Al2O3 ➜ 4Al + 3O2 (Overall Reaction)
From Text Books
Acids and Bases
PH Scale

From Text Books
Indicator Colour Change
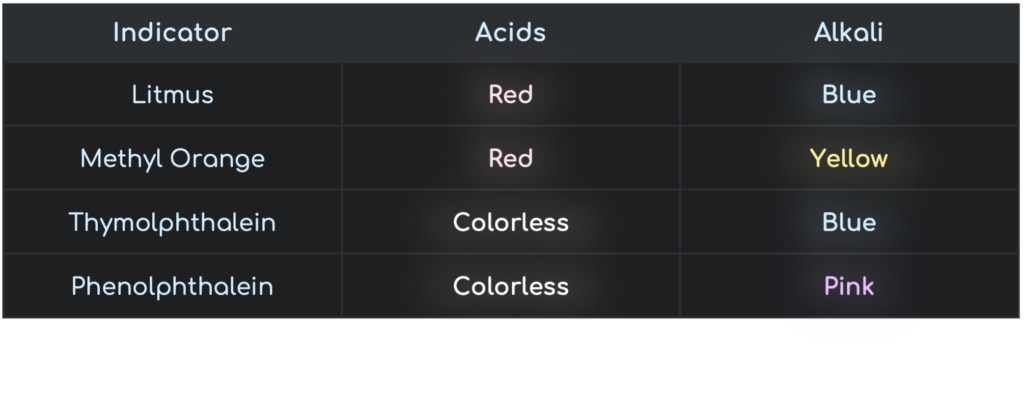
From Text Books
Difference between Strong Acids and Weak Acids
Acids contain Hydrogen ions. In solutions of strong acids, all the molecules become ions. In solutions of weak acids, only some do. The higher the concentration of hydrogen ions, the lower the pH.
Difference between Strong Bases and Weak Bases
Bases contain Hydroxide ions. If Solution A has a higher PH than Solution B, Solution A contains the most ions. The higher the concentration of hydroxide ions, the higher the pH.
From Text Books
Typical Acid Reactions
- With Metals: Acid + Metal ➜ Salt + Hydrogen
- With Bases: Acid + Base ➜ Salt + Water
- With Carbonates: Acid + Carbonate ➜ Salt + Water + Carbon dioxide
Typical Base Reactions
- Bases react with acids, and give salt and water.
- Bases such as sodium, potassium, and calcium hydroxides react with ammonium salts, giving out ammonia gas.
Neutralisation
Neutralisation is a reaction with acid that gives water as well as a salt. So the reactions of bases and carbonates with acids are neutralisations.
From Text Books
Oxides
From Text Books
Oxides are compounds containing oxygen and another element. In general, metals react with oxygen to form basic oxides. (Examples: Copper(II) oxide, CuO + 2HCl ➜ CuCl2 + H2O). Non-metals react with oxygen to form acidic oxides. (Examples: C + O2 ➜ CO2 OR S + O2 ➜ SO2)
© Copyright 2024 - Made with Passion
