Benefits of networking Devices, Types of Networks (PAN, LAN, MAN, WAN), client-server and peer-to-peer models, thin-client and thick-client, bus, star, mesh and hybrid topologies, cloud computing, use of wireless and wired networks, Ethernet Collisions, bit streaming,erences between the World Wide Web (WWW) and the Internet, hardware that is used to support the Internet...
Networking
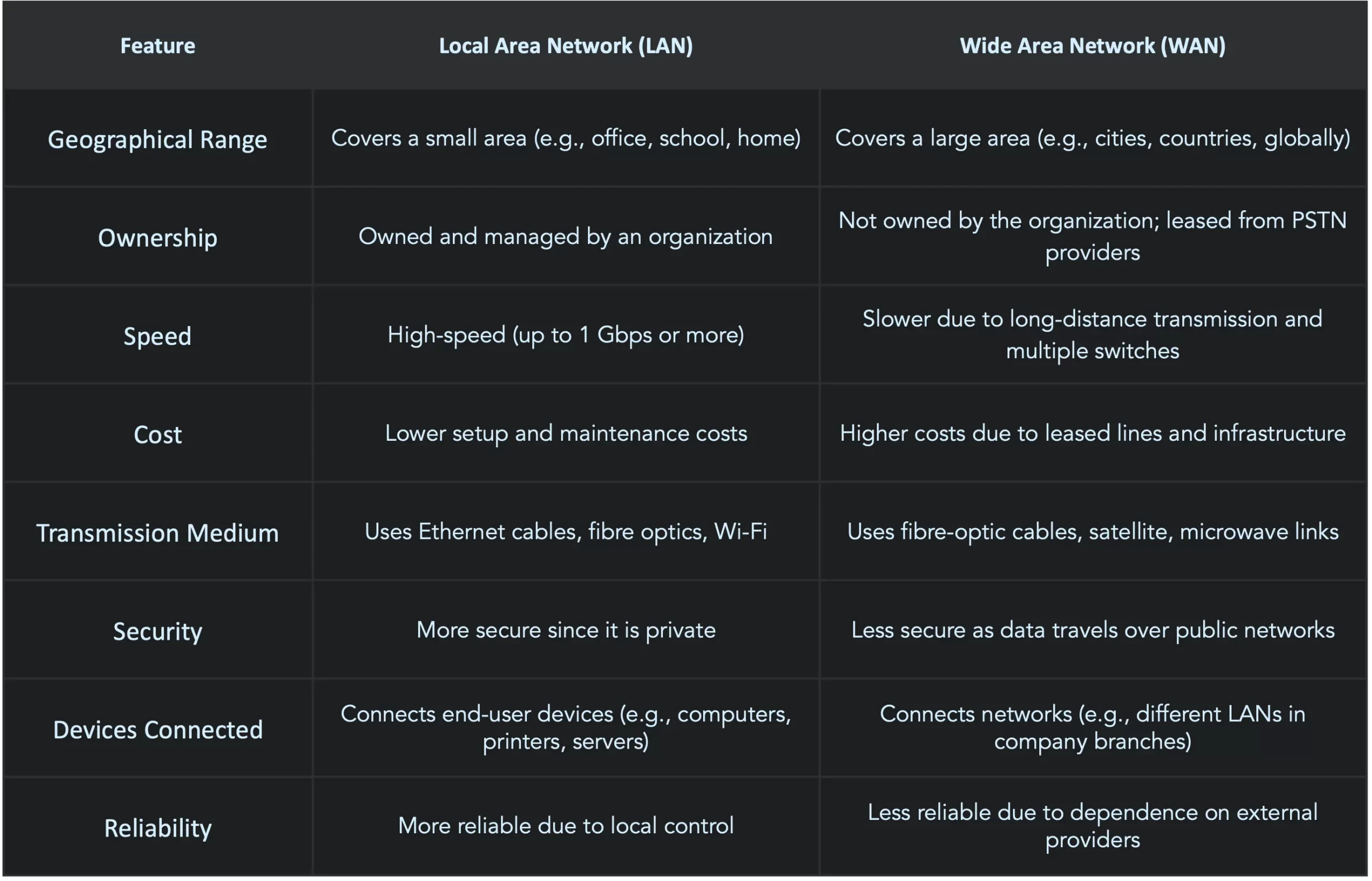
Local Area Network (LAN)
An organization or company will use a LAN within a site or branch. It will be owned by the organization or company and may be one of several individual LANs at the same site. The transmission medium can be twisted pair cable or WiFi. The LAN will include a device that enables connections to other networks. End-systems connected to the LAN will be user systems or servers.
Benefits
- Secure Communication – Data stays within the organisation, reducing external threats.
- No Lease: It will be owned and maintained by the organisation or company.
- Resource Sharing – Enables sharing of files and printers across connected devices. (Files/Print Server)
- Software Sharing – Installing software on an application server can save the expense of installing it on each PC.
- Reliability – Minimal interference as data transmission is limited to a small geographical area.
Drawbacks
- Setup Costs – Initial installation and hardware (switches, routers) can be expensive.
Security Risks (Internal) – While external threats are lower, insider attacks (e.g., unauthorised access).
From Text Books and Notes
Wide Area Network (WAN)
An organization or company will use this technology to connect sites or branches. It won’t be owned by the organization or company; instead, it will be leased from a public switched telephone network company (PSTN). The PSTN will provide a dedicated communication link using fiber-optic cable. Transmission within the wide area network (WAN) will occur from one switch to another, and a switch will connect the WAN to each site. There won’t be any end-systems directly connected to the WAN.
Benefits
- Resource Sharing – Users can access remote computers with required application software or stored data.
- Remote Data Access – Enables retrieval of data from centralised archives or servers.
- Interconnectivity and Speed – Connects multiple company branches/sites efficiently. Uses fibre-optic cables for fast, reliable data transfer.
Drawbacks
- Lease – Organisations must lease network services from public switched telephone network (PSTN) providers.
- Complex Infrastructure – Requires specialised hardware (e.g., switches) and skilled management.
From Text Books and Notes
Differences between WAN and LAN
From Text Books
What is the Client-Server Model?
In the client-server model, at least one computer acts as a server, providing services, applications, or resources. (P1) Other computers, known as clients, request and use these services from the server. (P2) The server manages and processes client requests, enabling efficient resource sharing and communication within a network.
From Past Papers
Two Options of How the client functions
Thin-client
A thin-client chooses an application to run on the server (P1) it then sends input data to the server when requested by the application. (P2) and receives output from the application. (P3)
Thick-client
A thick client chooses an application provided by the server. (P1) It may perform processing before running the application on the server and after receiving its output. (P2) Possibly downloads the application from the server and the application itself. (P3)
From Text Books
The benefits Client-Server Model?
From Past Papers
Benefits
- intranet capability
- Internet monitoring
- centralised back-up
- files and resources are centralised
- creation of security / manage security
- Users needs username and password to access network
- Reducing the server’s resource consumption reduces the client’s burden.
- Clients can be less resource-intensive machines, requiring less power, which makes them less expensive to purchase.
Topologies
Data Transfer
Simplex Data Transfer occurs when data can be sent in one direction only (from ‘A’ to ‘B’ only or ‘B’ to ‘A’ only). An example of this would be sending data from a computer to a printer.
Half-duplex Data Transfer occurs when data is sent in both directions but not at the same time (data can be sent from ‘A’ to ‘B’ and from ‘B’ to ‘A’, but the data can’t be transferred at the same time). An example of this would be a walkie-talkie, where a message can be sent in one direction only at a time; but messages can be both received and sent.
Full-duplex Data Transfer occurs when data can be sent in both directions at the same time (data can be sent from ‘A’ to ‘B’ and from ‘B’ to ‘A’ along the same transmission line simultaneously). An example of this would be a broadband internet connection.
From Text Books
Serial and parallel Data Transfer
Serial data transmission occurs when data is sent one bit at a time over a single wire/channel. bits are sent one after the other as a single stream.

Parallel data transmission occurs when several bits of data (usually one byte) are sent down several channels/wires all at the same time. each channel/wire transmits one bit.
From Text Books
Point to Point
A point-to-point connection is a dedicated link that offers a simplex or duplex transmission mode. In this connection, a message can only be sent unicast.
From Text Books
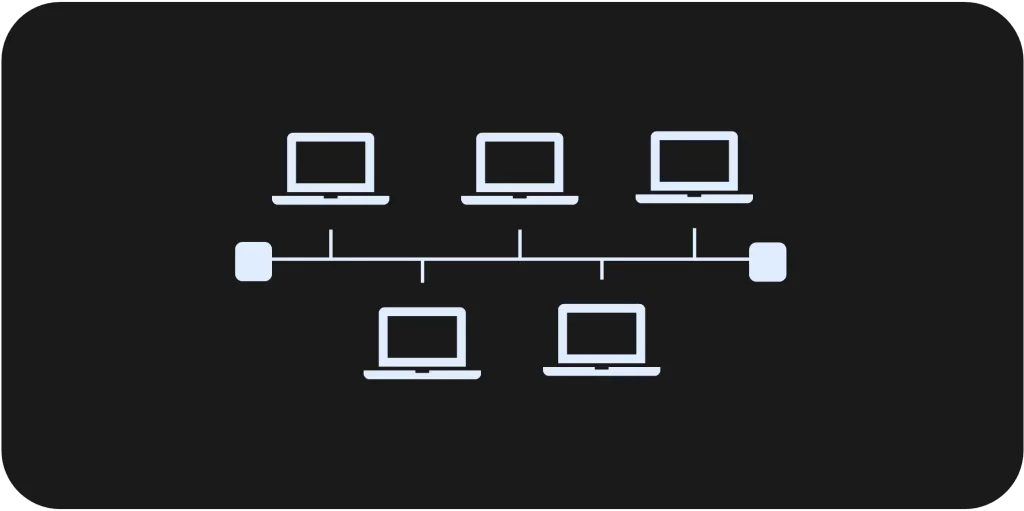
Bus Topology
- Topology Structure: A multi-point connection with a single shared link, lacking direct connections between end-systems (Nodes).
- Message Transmission: Messages are broadcast, even if intended for a single end-system (Node) and stopped by the Terminator.
- Network Resilience: Partially resilient; end-system or connection faults don’t affect other users, but backbone failure/adding nodes temporarily disrupts the entire network.
From Text Books
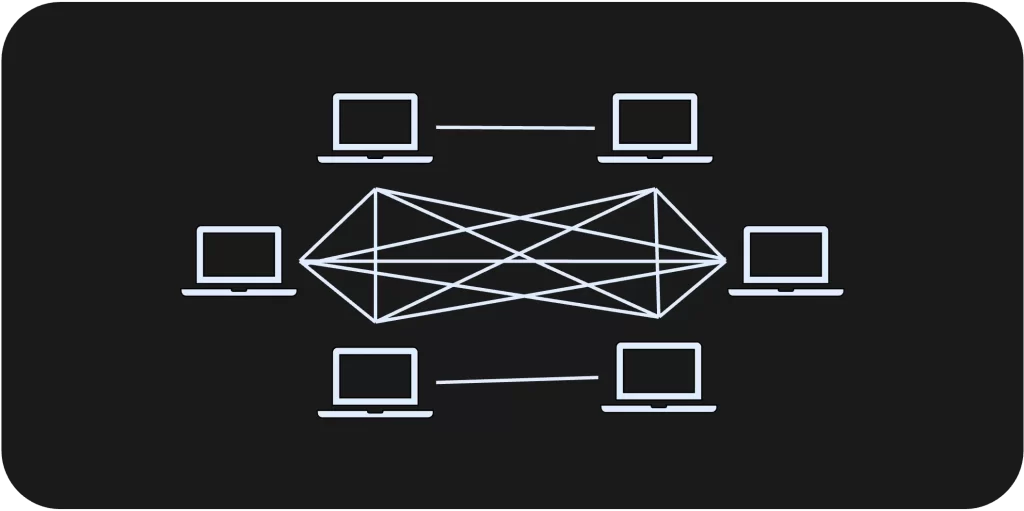
Mesh Topology
- Mesh Topology: Each end-system connects to every other end-system, enabling full-duplex transmission.
- Message Transmission: Messages can be unicast, multicast, or broadcast, depending on the communication needs.
- Advantages: Fast communication, high security, and reliable data transfer with fault tolerance.
- Disadvantages: High maintenance complexity, expensive infrastructure, and difficult installation and scalability.
From Text Books
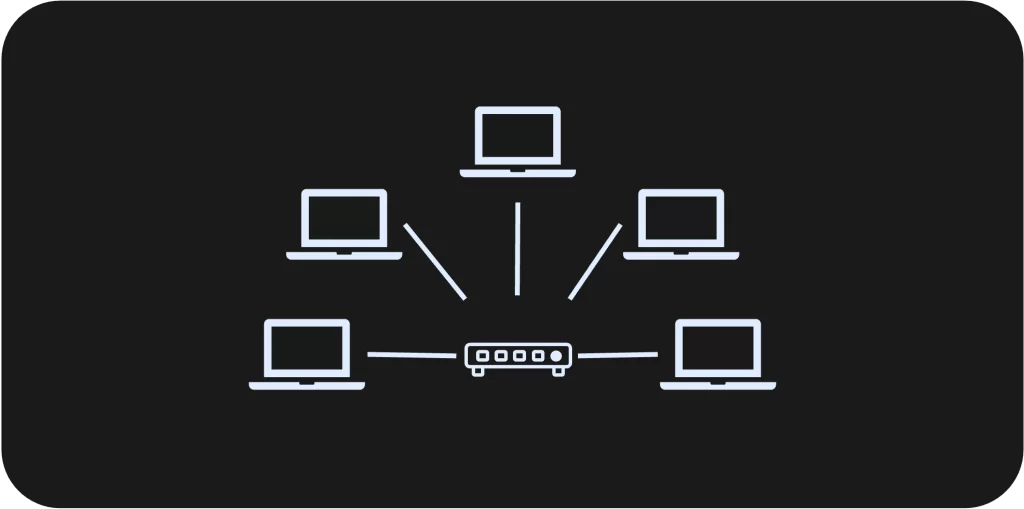
Star Topology
- Topology Structure: Each end-system is connected to a central device via a point-to-point link.
- Transmission Mode: Supports duplex transmission with unicast, multicast, and broadcast capabilities.
- Fault Tolerance: End-system or connection failure doesn’t impact other systems, but the central device must remain operational.
- Scalability (Advantage): Easy to scale by adding new devices with a single connection to the central device.
- Installation (Advantage): Easy to install, making it a popular choice for modern networks.
- Costs (Disadvantage): Higher cost due to additional hardware (Switches) and central device dependency, meaning network failure if the central device fails.
From Text Books
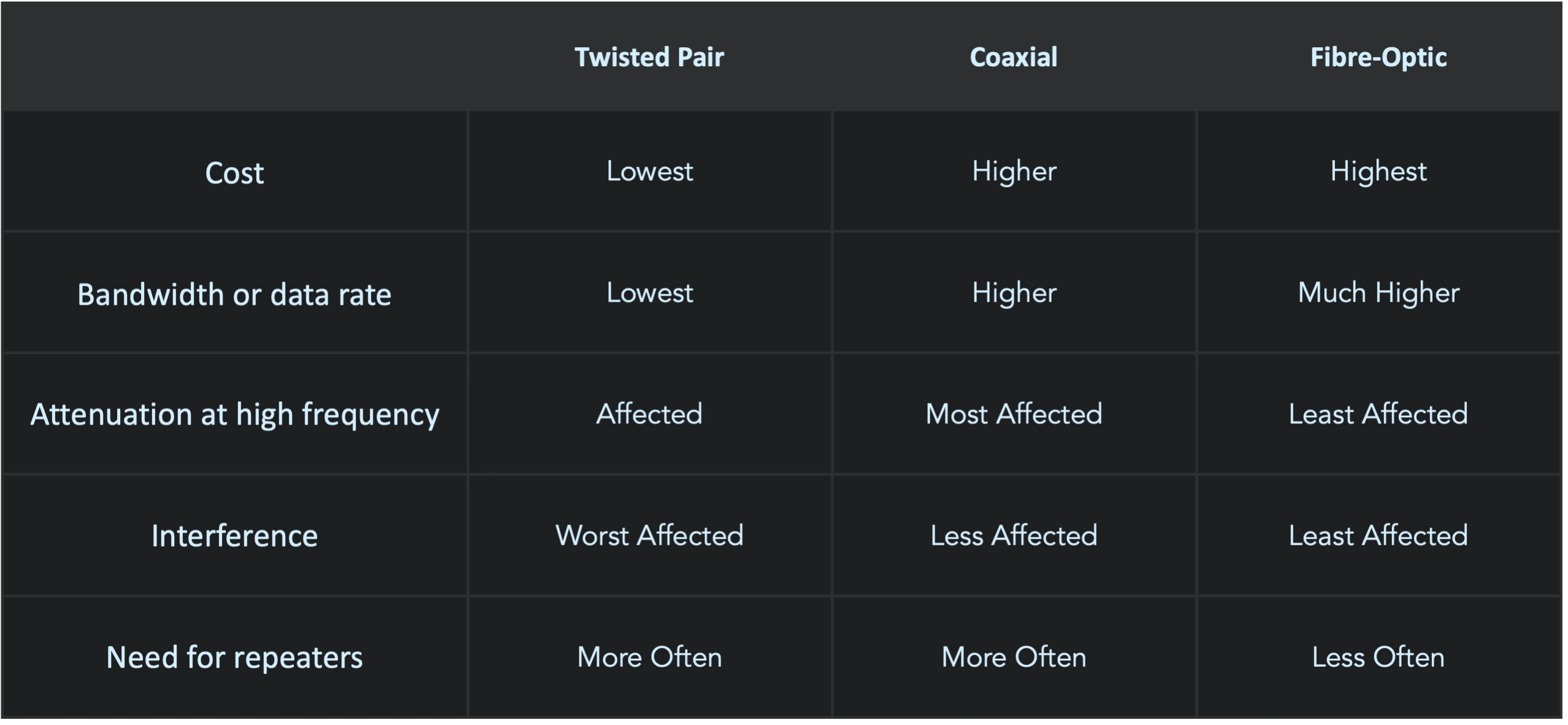
Transmission Media
Difference between Twisted pair, Coaxial, Fibre-optic
From Text Books
© Copyright 2024 - Made with Passion
