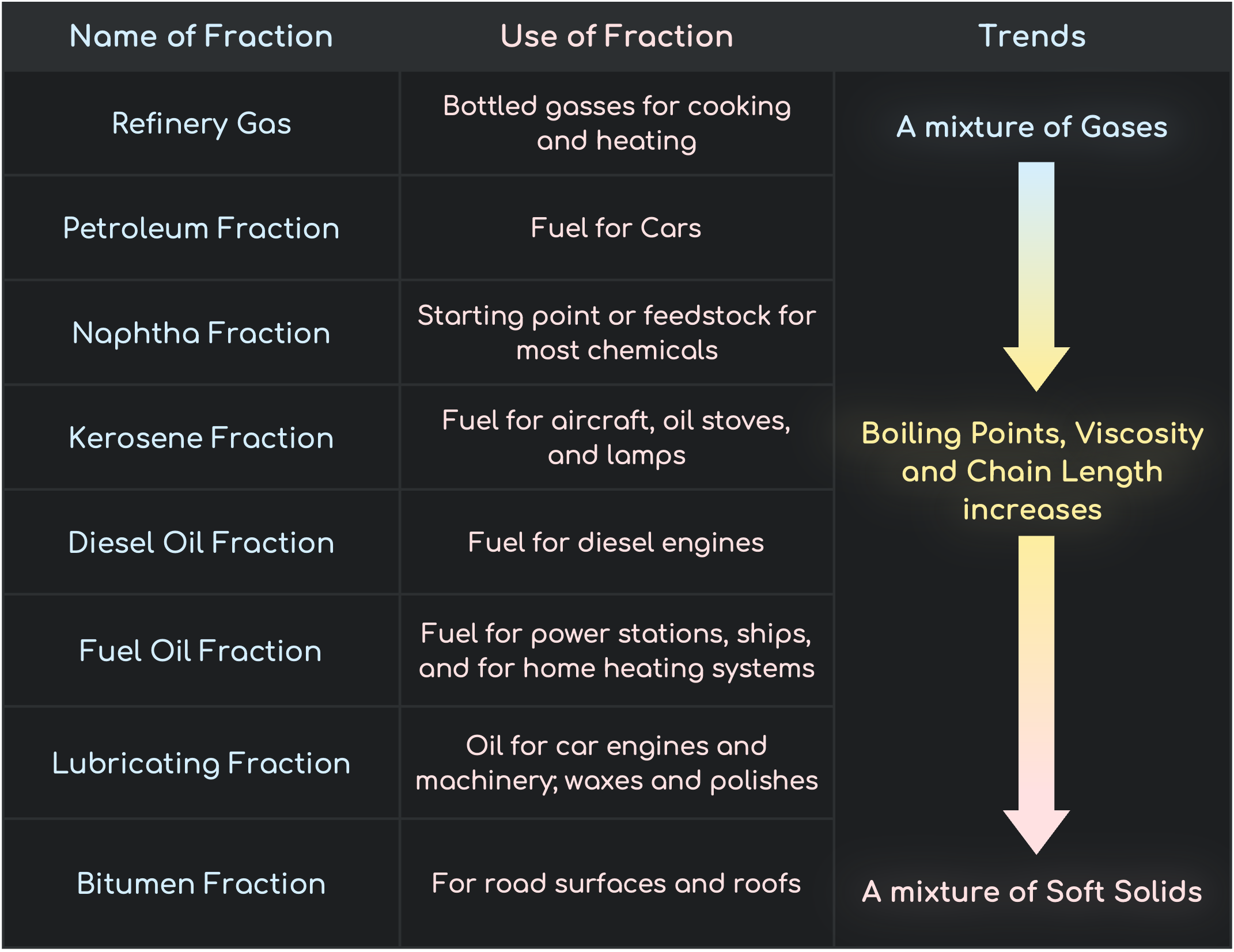
Refining Petroleum
Fractions and Trends
Chain Length, Boiling Points and Viscosity increase down the Fractions. Volatility and Flammability decrease down the Fraction.
- Refinery Gas has the lowest boiling Point and Viscosity but is the most Volatile and is highly flammable
- Bitumen has the highest boiling Point and Viscosity but is the least Volatile and is not as flammable as refinery gas
From Text Books
Organic Compounds
Functional Groups
A functional group is an atom or group of atom in a molecule that dictate how the compounds will react.
Homologous Series
A homologous Series is a family of similar compounds that have the same functional group, so have similar chemical Properties.
- All the compounds fit the same general formula.
- The compounds show a trend in physical properties, as the chain gets longer. Melting and boiling points rise. Viscosity increases – they flow less easily. Flammability decreases – they burn less easily
From Text Books
Reactions between the four Organic Compound Families
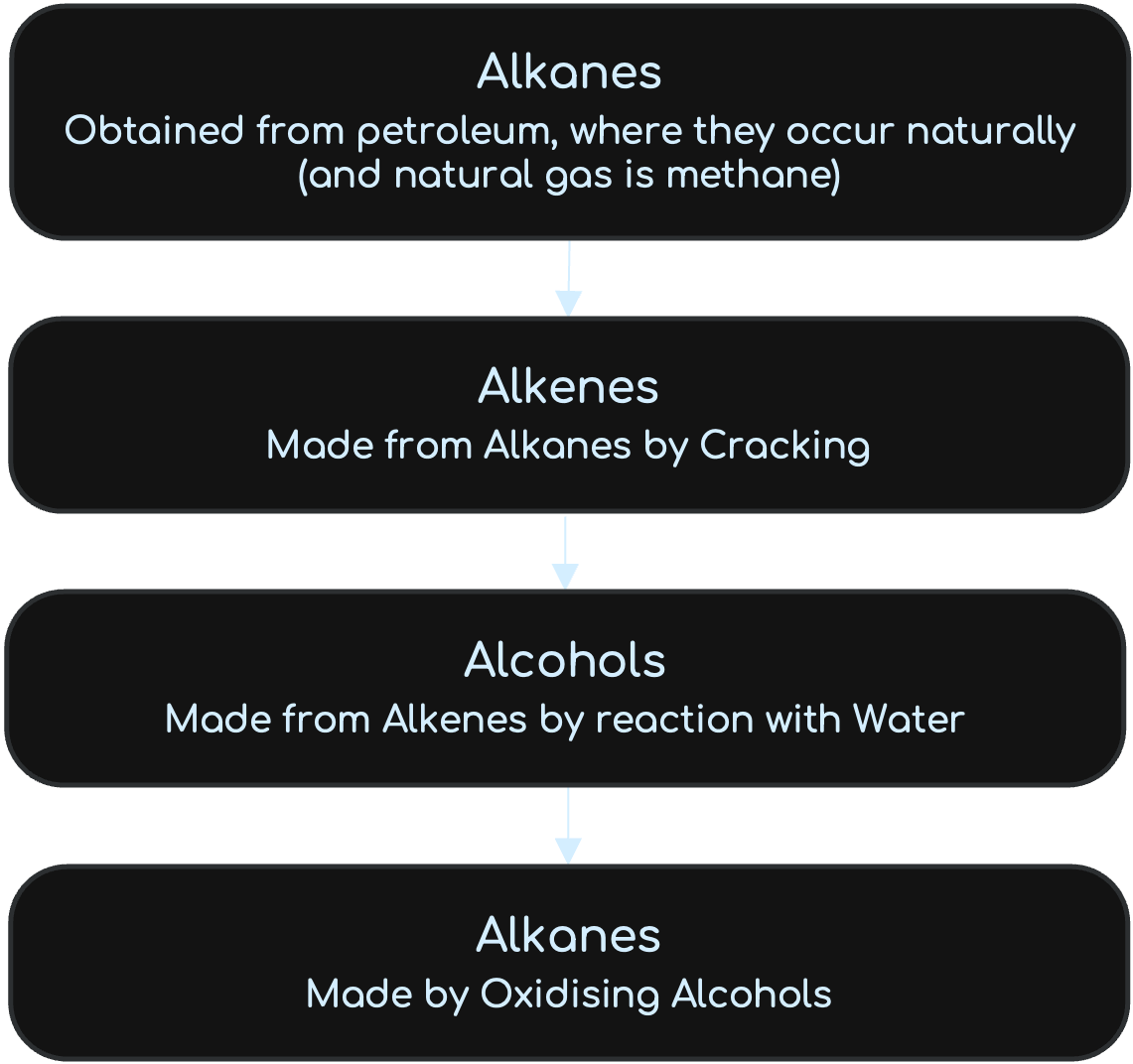
From Text Books
Alkanes
Alkanes contain only carbon and hydrogen, so they are hydrocarbons. The bonds between their carbon atoms are all single bonds. Alkanes are saturated as they only have a single carbon bond. (General Formula: CnH2n+2 )
Here are the First 6 Alkanes:
- Methane (CH4)
- Ethane (C2H6)
- Propane (C3H8)
- Butane (C4H10)
- Pentane (C5H12)
- Hexane (C6H14)
From Text Books
Alkenes
Alkanes contain only carbon and hydrogen, so they are also hydrocarbons. All alkenes contain carbon – carbon double bonds. Alkanes are unsaturated as they only have a double carbon bond. (General Formula: CnH2n )
Formation of Alkenes:
Alkenes can be formed by cracking Alkanes with steam and temperatures above 800 degrees Celcius.
Test for Alkenes:
Alkenes can be tested using Bromine Water. The orange colour of the solution turns colourless when alkenes are added due to addition reaction.
Here are the First 6 Alkenes:
- Ethene (C2H4)
- Propene (C3H6)
- Butene (C4H8)
- Pentene (C5H10)
- Hexene (C6H12)
- Heptene (C7H14)
From Text Books
Alcohols
The alcohols are not hydrocarbons. They are like the alkanes, but with an OH group. The OH group is their functional group. (General Formula: CnH2n+1 OH). Ethanol can be formed by fermentation or by Hydration.
Fermentation:
(Glucose ➜ Ethanol + Carbon dioxide + Energy)(Conditions: 25-35°C, Enzymes in Yeast)
Hydration:
(Ethene + Water ➜ Ethanol) (Conditions: 570°C, 50-60 ATM and Phosphoric Acid as catalyst)
Uses of Alcohols:
- It is a good solvent. It dissolves many substances that do not dissolve in water.
- Burns Readily in Oxygen and gives out a lot of heat. Hence, they can be used as fuel.
- It can be used in sanitizers and wipes, as it can kill bacteria and viruses.
Here are the First 4 Alcohols:
- Methanol (CH3OH)
- Ethanol (C2H5OH)
- Propanol (C4H7OH)
- Butanol (C4H9OH)
From Text Books
Carboxylic acids
The carboxylic acids are also not hydrocarbons, as they don’t have any hydrogen and carbon atoms. All carboxylic acids contain the COOH group. COOH is their functional group. (General Formula: CnH2nO2)
Formation of Carboxylic acids:
Carboxylic Acids are formed when Ethanol is left standing in air and bacteria oxidises it. This is called Fermentation.
Here are the First 4 Carboxylic acids:
- Methanoic (HCOOH)
- Ethanoic (CH3COOH)
- Propanoic (C2H5COOH)
- Butanoic (C3H7COOH)
Esters
Carboxylic Acids react with Alcohols to give compounds called Esters. The Esters name contains the Alcohol First and the Acid at the last. An Example: Propyl Ethanoate.
- Carboxylic Acid + Alcohol ⇌ Ester + Water
- Ethanoic Acid + Propanol ⇌ Propyl Ethanoate + Water
From Text Books
© Copyright 2024 - Made with Passion
